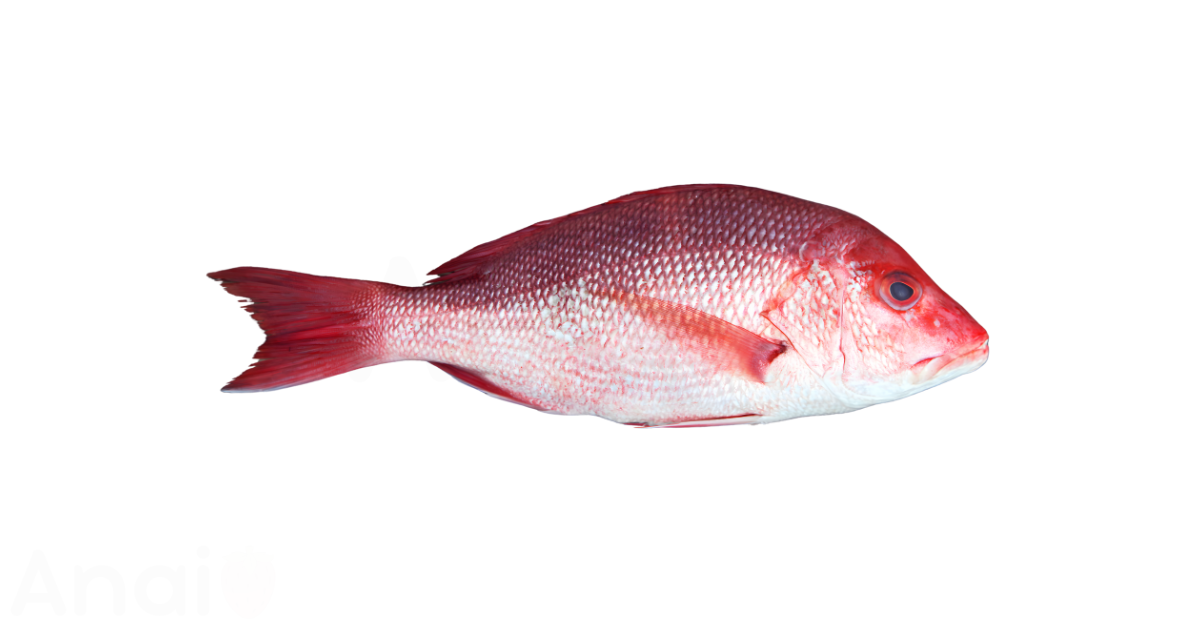
Is Snapper Good for You?
Yes, snapper is an excellent and healthy food choice. This popular white fish is a low-calorie, lean source of high-quality protein. A single 100-gram (3.5-ounce) serving of cooked snapper contains 128 calories and a remarkable 26 grams of protein, with very little fat. It is packed with essential nutrients, including heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, the powerful antioxidant selenium, potassium, and a range of B vitamins, especially Vitamin B12. While there are some concerns about mercury levels, red snapper is considered safe for occasional consumption, about one to two times per week for the general population (Harris-Ray, 2024).
This article will provide a comprehensive look at the benefits and nutritional profile of snapper. We will explore topics such as the 13 effective health benefits of snapper, detailed snapper nutrition facts, potential snapper risks and side effects, and suitable snapper substitutes. We will also cover popular snapper diets, proper snapper storage tips, 7 simple snapper home remedies, the role of snapper and weight management, and the use of snapper for specific health conditions. This article contains the latest information as of March 2026.
13 Effective Health Benefits of Snapper
Snapper is more than just a delicious, mild-flavored fish; it’s a nutrient-dense food that can play a significant role in a healthy diet. The following health benefits are fact-checked and supported by nutritional data and publications from health and science authorities.
1. Supports Thyroid Health
Snapper is an incredible source of selenium, a mineral that is critical for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland. A single 100-gram serving of snapper provides 49 micrograms of selenium, which is nearly 70% of the daily recommended amount for adults (Aquapazza, 2022). The thyroid gland requires selenium to produce its hormones, which regulate metabolism throughout the body (Harris-Ray, 2024).
2. Boosts the Immune System
The high selenium content in snapper also supports a strong immune system by promoting healthy white blood cell function (Harris-Ray, 2024). In addition to selenium, snapper is a source of Vitamin A, another nutrient vital for immune health. A 3-ounce serving of cooked red snapper can provide up to 14% of the recommended daily allowance of vitamin A for an adult woman.
3. Promotes Heart Health
Snapper is an excellent choice for a heart-healthy diet. It is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to significantly decrease the risk of heart disease, atherosclerosis, and high cholesterol. It’s also low in saturated fat, containing only 0.37 grams per 100g serving (Foodstruct, n.d.). Furthermore, its high potassium content helps manage blood pressure.
4. Strengthens Bones
Potassium plays a key role in preventing osteoporosis and strengthening bone mineral density, and snapper is a great source of it (Harris-Ray, 2024). A 100-gram fillet contains 522 milligrams of potassium. Additionally, snapper is rich in Vitamin B12, which research has shown also helps promote bone health (Palumbo, 2020).
5. Aids in Weight Management
As a lean source of high-quality protein, snapper is an ideal food for weight management. Protein is known to increase feelings of fullness, which can help reduce overall calorie intake. With 26 grams of protein and only 128 calories in a 100-gram serving, snapper helps you feel satisfied without consuming excess calories or fat (Palumbo, 2020).
6. Helps Prevent Anemia
Snapper is a “vitamin B12 superstar”. This vitamin is essential for producing red blood cells, and a deficiency can lead to conditions like megaloblastic anemia. A 100-gram serving of snapper delivers an impressive 3.5 micrograms of Vitamin B12, which is 146% of the recommended Daily Value (Harris-Ray, 2024).
7. Improves Cognitive Function
The unique combination of nutrients in snapper can help boost brain health. The blend of Vitamin A, selenium, Omega-3 fatty acids, and potassium contributes to a healthy nervous system and improved cognitive function (Harris-Ray, 2024). Some studies also suggest that Vitamin B12 can help slow mental decline (Palumbo, 2020).
8. Protects Eye Health
The Vitamin A in snapper is crucial for maintaining healthy vision. Eating a diet with adequate amounts of Vitamin A may decrease the risk of developing serious eye disorders, including cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (Aquapazza, 2022).
9. Reduces Inflammation
Inflammation is a root cause of many chronic diseases. The omega-3 fatty acids found in snapper are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating snapper into your diet can help reduce systemic inflammation and lower your risk of related conditions (Palumbo, 2020).
10. May Lower Blood Pressure
Snapper’s high concentration of both potassium and omega-3 fatty acids makes it a powerful food for managing blood pressure. Potassium helps to balance sodium levels and relax blood vessels, while omega-3s also contribute to lower pressure, reducing strain on the cardiovascular system (Harris-Ray, 2024).
11. Supports DNA Synthesis
Vitamin B12 is not only important for red blood cells but is also a fundamental building block for DNA synthesis (Palumbo, 2020). This process is essential for the growth and repair of every cell in your body, making the high B12 content in snapper incredibly valuable.
12. Rich in Powerful Antioxidants
Selenium functions as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals (Palumbo, 2020). This antioxidant activity can help prevent the DNA damage that may lead to chronic diseases such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and heart disease (Aquapazza, 2022).
13. Helps Build and Repair Tissues
The high-quality protein in snapper provides the essential amino acids your body needs to build and repair tissues, including muscle, skin, and organs. A single 100-gram serving provides over half of the daily value for protein, making it an efficient way to support your body’s structural needs (Foodstruct, n.d.; Palumbo, 2020).
Snapper Nutrition Facts
The many health benefits of snapper can be further explained through their impressive nutrition facts, as analyzed in detail below:
Snapper nutrition table
The following table provides a detailed breakdown of the key nutritional components found in a standard serving of cooked snapper, as well as per 100 grams. A typical serving size is considered to be one fillet, which is approximately 170 grams (6 ounces).
| Nutrient | Per Serving (170g) | DRI % (Serving) | Per 100 grams | DRI % (100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 218 kcal | 11% | 128 kcal | 6% |
| Protein | 44.2 g | 88% | 26 g | 52% |
| Carbs | 0 g | 0% | 0 g | 0% |
| Total Fat | 2.9 g | 4% | 1.7 g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 80 mg | 27% | 47 mg | 16% |
How many calories are in snapper?
Snapper is a low-calorie food, making it an excellent choice for weight management. A 100-gram portion of cooked snapper contains only 128 calories, which is just 6% of the daily recommended intake for a 2,000-calorie diet. A standard 170-gram fillet provides 218 calories. To burn off the 128 calories from a 100g serving, you would need to do approximately 13 minutes of jogging or 35 minutes of walking at a moderate pace.
How much protein is in snapper?
Snapper is exceptionally rich in high-quality, lean protein. A 100-gram serving delivers 26 grams of protein, fulfilling over half (52%) of the daily recommended intake. A single 170-gram fillet contains an impressive 44.2 grams of protein, which is 88% of the daily requirement. This substantial protein content is crucial for muscle repair, cell generation, and maintaining a feeling of fullness.
How many carbs are in snapper?
Snapper contains zero carbohydrates. This makes it an ideal food for low-carb and ketogenic diets, as it provides essential nutrients without impacting blood sugar levels.
How much fat is in snapper?
Snapper is a very lean fish with a low total fat content. A 100-gram serving has only 1.7 grams of fat. Importantly, a significant portion of this fat consists of healthy, unsaturated fats, including beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
| Fat Type | Per 100 grams |
|---|---|
| Total Fat | 1.7 g |
| Saturated Fat | 0.37 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat (MUFAs) | 0.32 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat (PUFAs) | 0.59 g |
Is snapper high in cholesterol?
Snapper contains a moderate amount of cholesterol. There are 47 milligrams in a 100-gram portion and 80 milligrams in a 170-gram fillet. This represents 16% and 27% of the daily recommended intake, respectively. For most people, dietary cholesterol has less impact on blood cholesterol levels than saturated fat, and since snapper is very low in saturated fat, it remains a heart-healthy choice.
Minerals in snapper
Snapper provides a wealth of essential minerals, particularly selenium and potassium, which are vital for numerous bodily functions.
| Mineral | Amount (per 100g) | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Selenium | 49 mcg | Acts as a powerful antioxidant, supports thyroid function, and boosts the immune system. |
| Potassium | 522 mg | Helps regulate blood pressure, supports muscle contractions, and maintains fluid balance. |
| Phosphorus | 201 mg | Crucial for building strong bones and teeth, and helps filter waste in the kidneys. |
| Magnesium | 37 mg | Involved in over 300 biochemical reactions, supporting nerve function and bone health. |
In summary, snapper is an outstanding source of selenium, providing nearly 90% of the daily value in a single 100g serving. It is also an excellent source of potassium, which is critical for heart and muscle health.
Vitamins in snapper
The vitamin profile of snapper is dominated by B vitamins, which are essential for energy metabolism and overall health.
| Vitamin | Amount (per 100g) | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 | 3.5 mcg | Essential for creating red blood cells and DNA, and for maintaining healthy nerve cells. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.46 mg | Important for brain development and function, and helps the body make serotonin and norepinephrine. |
| Vitamin A | 35 mcg | Vital for vision, immune function, reproduction, and cellular communication. |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.87 mg | Helps convert food into energy and is critical for making blood cells. |
Snapper is a true powerhouse of Vitamin B12, with a 100g serving providing 146% of the daily recommended value. It is also a very good source of Vitamin B6.
Snapper Risks and Side Effects
While snapper is a nutritious fish, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of. The most significant risk is ciguatera fish poisoning, which is caused by eating reef fish that have accumulated ciguatoxin. This toxin is tasteless, odorless, and cannot be destroyed by cooking or freezing. Symptoms can range from gastrointestinal distress to severe neurological issues, such as the bizarre sensation of temperature reversal where hot things feel cold. To minimize risk, it is advisable to avoid eating large reef fish (over 5 pounds) and to never consume the parts where toxins concentrate, like the liver, head, or intestines.
Another concern is mercury. Red snapper can contain mercury, a heavy metal that can be harmful to the nervous system in high doses. For this reason, regulatory bodies often advise that pregnant women and young children should consume snapper in moderation, typically no more than once or twice a week.
Finally, like all seafood, snapper is a potential allergen. Individuals with a fish allergy can experience reactions ranging from mild itching and hives to severe anaphylaxis. If you have a known fish allergy, you must avoid snapper entirely.
Debunking myths about snapper
Myth: All snappers are dangerously high in mercury.
Fact: While red snapper does contain some mercury, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) lists it in the “Good Choices” category for weekly consumption. This means that for the general population, eating one serving of snapper per week is considered safe. Its mercury levels are significantly lower than those in fish from the “Choices to Avoid” category, such as shark, swordfish, or king mackerel.
Myth: You can eliminate toxins from snapper by cooking it thoroughly.
Fact: This is a dangerous misconception. The primary toxin of concern in snapper, ciguatoxin, is heat-stable. This means no amount of cooking, freezing, smoking, or marinating will destroy or remove the toxin. The only effective prevention method is to avoid consuming high-risk reef fish.
Snapper Substitutes
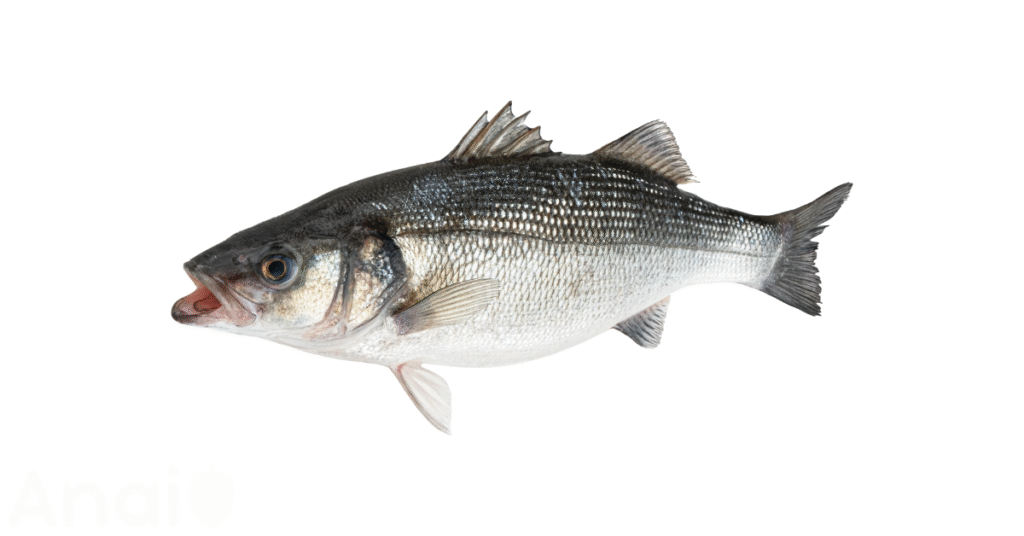

If snapper is unavailable or if you’re looking for an alternative, several other white fish offer a similar texture and flavor profile.
| Substitute | Protein (per 100g) | Omega-3s (per 100g) | Calories (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snapper | 26 g | 310 mg | 128 |
| Grouper | 25 g | 410 mg | 118 |
| Sea Bass | 24 g | 850 mg | 124 |
| Cod | 23 g | 230 mg | 105 |
The best grouper for a snapper substitute is the red grouper, which has a mild, slightly sweet flavor very similar to snapper. It holds up well to various cooking methods like grilling, baking, and frying. A key benefit of grouper is its slightly higher omega-3 content. However, it is also a reef fish and carries a similar risk of ciguatera poisoning, and it can sometimes be more expensive than snapper.
With its firm, meaty texture and moderately high oil content, sea bass is another excellent substitute. Its primary advantage is a significantly higher concentration of healthy omega-3 fatty acids compared to snapper. It can be prepared in the same ways as snapper, though it may have a slightly more pronounced flavor. A drawback is that sea bass can also be a pricier option.
For a more budget-friendly and widely available option, cod is a suitable replacement. Cod has a milder flavor and a more delicate, flaky texture than snapper. Its main benefit is its lower calorie count and wide availability. The primary drawback is that it has a lower protein and omega-3 content and its delicate texture may cause it to fall apart more easily, making it less ideal for grilling.
Popular Snapper Diets
How to add snapper safely into your diet? Choosing the right diet is important to ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs while also enjoying the foods you eat. Here are a few of the available snapper-friendly diet options:
- The Mediterranean Diet
- The Paleo Diet
- The Ketogenic (Keto) Diet
| Diet | Primary Focus | Snapper’s Role | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean Diet | Emphasizes whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, healthy fats from olive oil, and fish. | An ideal source of lean protein and heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, recommended for regular consumption. | Promotes heart and brain health, linked to longevity, offers balanced and varied nutrition. | Can be high in calories if portion sizes of healthy fats and other foods are not monitored. |
| Paleo Diet | Mimics the eating patterns of Paleolithic ancestors, focusing on lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. | A primary source of high-quality animal protein and essential fats, fitting perfectly within the diet’s framework. | Encourages whole-food consumption, may lead to weight loss and improved glucose tolerance. | Highly restrictive, as it eliminates entire food groups like dairy, grains, and legumes. |
| Ketogenic (Keto) Diet | A very low-carbohydrate, high-fat, and moderate-protein eating plan designed to induce ketosis. | An excellent protein source due to its zero-carb content and healthy fats, helping to meet protein goals without adding carbs. | Often effective for rapid weight loss and may improve blood sugar control in some individuals. | Extremely restrictive and can be difficult to maintain; potential for “keto flu” and nutrient deficiencies. |
The Mediterranean Diet is frequently celebrated by health professionals for its balanced approach and long-term sustainability. It isn’t just a diet but a lifestyle that includes a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods. Snapper fits seamlessly into this plan, often baked or grilled with olive oil, lemon, and herbs, reflecting the simple and healthy cooking methods favored in the region.
Based on the presumed diet of early humans, the Paleo Diet eliminates all processed foods, grains, dairy, and legumes. Snapper is a cornerstone of the Paleo protein intake, providing essential nutrients without any of the restricted food groups. This diet’s focus on whole, unprocessed foods is a major benefit, though its restrictive nature can be a challenge for some.
The Ketogenic (Keto) Diet drastically reduces carbohydrate intake to shift the body’s metabolism toward burning fat for energy. Because snapper contains no carbohydrates, it is a perfect food for keto followers. It provides necessary protein and fats without disrupting ketosis, making it a versatile ingredient for keto-friendly meals. However, the diet’s rigidity requires careful planning to ensure nutritional adequacy.
How to Cook Snapper?
Snapper is a remarkably versatile fish that shines with several cooking methods. Choosing the right technique can enhance its mild, sweet flavor and firm, flaky texture. Nutrient loss is generally minimal with most of these methods, especially when compared to deep-frying or boiling.
Baked snapper is an excellent method for keeping the fish tender and moist. A great tip is to lay the fillets on a bed of lemon slices in a baking dish. This protects the fish from direct heat, gently steaming it while infusing it with citrus flavor. Baking at a moderate temperature, around 375°F for 15-20 minutes, preserves the most nutrients and results in buttery-soft fish that flakes easily.
Roasted snapper uses a higher temperature, typically 400°F or more, to cook the fish. This method is faster, often taking just 10-15 minutes, and helps to create a lightly browned exterior while keeping the inside juicy. It’s an efficient way to cook snapper and also results in minimal nutrient loss. Drizzling the fillets with olive oil and white wine before roasting adds moisture and a rich flavor.
Pan-seared snapper is the fastest route to a delicious meal, often ready in under 10 minutes. The key is to pat the fillets completely dry and use a very hot skillet. This technique creates an irresistibly crispy, golden-brown skin while the flesh remains flaky and moist. While the high, direct heat can cause slightly more nutrient degradation than baking, the extremely short cooking time helps to preserve much of its nutritional value.
Grilled snapper is perfect for achieving a smoky, charred flavor that complements the fish’s natural sweetness. Whether on an outdoor grill or an indoor grill pan, it’s important to oil the grates well to prevent the delicate fish from sticking. Grilling is a healthy, low-fat cooking method that does an excellent job of retaining the snapper’s nutrients.
Easy Snapper Recipes

Incorporating more fish into your diet is easy and delicious with these simple snapper recipes that deliver on flavor without requiring hours in the kitchen.
Breakfast ideas with snapper
A Snapper and Herb Scramble is a fantastic way to start the day with a high-protein meal. Simply flake leftover cooked snapper into your eggs as they scramble and finish with a sprinkle of fresh parsley or dill. For something a bit different, Flaked Snapper on Avocado Toast provides a great mix of healthy fats and protein. Just mix the fish with a squeeze of lemon juice and layer it over mashed avocado on whole-grain toast.
Lunch ideas with snapper
Snapper Fish Tacos make for a quick and satisfying lunch. Use baked or pan-seared snapper and flake it into warm corn tortillas with a crunchy slaw and a drizzle of lime crema. Another great option is a Mediterranean Snapper Salad. Toss chilled, cooked snapper chunks with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, olives, and a light lemon-herb vinaigrette for a refreshing and light meal.
Dinner ideas with snapper
A simple Baked Red Snapper with Lemon and Garlic is a classic that never fails. The fish is seasoned and baked to perfection in under 20 minutes for a healthy and flavorful main course. For a quicker option, Pan-Seared Snapper with a Honey Mustard Glaze offers crispy skin and a tangy-sweet sauce that comes together in minutes. If you’re feeling more adventurous, Roasted Red Snapper Italian Style with white wine, rosemary, and lemon creates a deeply flavorful and aromatic dish.
Simple tips to add snapper to your diet
For busy people who don’t have the time to implement any of the previous meal ideas, there are simple tips to add Snapper to their diet.
- Flake leftover cooked snapper into a green salad to instantly boost its protein content.
- Toss chunks of snapper with your favorite pasta and a light olive oil or tomato-based sauce.
- Use snapper as the primary protein in a healthy grain bowl with quinoa, vegetables, and a flavorful dressing.
- Create quick and easy fish cakes by combining flaked snapper with mashed potatoes or breadcrumbs and pan-frying them.
- Stir cooked snapper into a simple vegetable or tomato soup just before serving for added flavor and nutrition.
- Make a simple snapper spread for crackers or sandwiches by mixing it with Greek yogurt, herbs, and a squeeze of lemon.
- Keep cooked and flaked snapper in the fridge to easily add to wraps or pitas for a quick protein source.
Snapper Storage Tips
Knowing how to cook snapper is only part of the equation; it’s equally important to know the best snapper storage tips to make those delicious meals last longer while ensuring safety.
Shelf life of snapper
- At room temperature: Raw fish should never be left at room temperature. It should be refrigerated or frozen as soon as possible after purchase.
- In the refrigerator: Fresh, raw snapper can be safely stored in the refrigerator for 1 to 2 days. Cooked snapper will last for 3 to 4 days.
- In the freezer: Properly frozen raw snapper maintains its best quality for 6 to 8 months. Leaner fish like snapper can last up to two years if vacuum-sealed, although quality may diminish over time.
How to store snapper?
Properly storing snapper is crucial to maintaining its freshness and preventing the growth of spoilage bacteria. The two main enemies of fresh fish are air and moisture. Your goal is to keep the fish as cold and dry as possible without freezing it (unless you plan to). Exposure to air can cause the fish to dry out, while excess moisture accelerates bacterial growth.
Always store snapper in the coldest part of your refrigerator, which is typically the bottom shelf towards the back. This location has the most stable temperature. To prevent any cross-contamination, ensure the fish is well-sealed and kept away from other foods. Never refreeze fish that has already been thawed.
How to refridgerate snapper?
To keep your snapper as fresh as possible in the refrigerator, follow these steps precisely.
- Remove the snapper from its original store packaging as soon as you get home.
- Rinse the fish under cold running water.
- Thoroughly pat the fish dry on all sides with paper towels. This step is critical as bacteria thrive in moisture.
- Place the dry fillets in a single layer inside a zip-top bag. Do not stack them.
- Press all the excess air out of the bag and seal it tightly.
- Place the bag on a tray or plate covered in ice or ice packs.
- Store the entire setup on the bottom shelf of your refrigerator. Replenish the ice as it melts.
How to freeze snapper?
Freezing is the best way to preserve snapper if you don’t plan to cook it within a couple of days.
- Start with the freshest fish possible. If the fish is whole, ensure it has been gutted and scaled.
- Rinse the fish under cold water and pat it completely dry with paper towels.
- Wrap the fish tightly in plastic wrap or aluminum foil to minimize air exposure. For best results and to prevent freezer burn, use a vacuum sealer if you have one.
- Place the wrapped fish into a heavy-duty freezer bag, pressing out any remaining air before sealing.
- Label the bag with the date of freezing.
- Place it in the coldest part of your freezer.
Signs of Spoilage in snapper
It is vital to be able to recognize when snapper has gone bad to prevent foodborne illness.
- Odor: The most reliable sign of spoilage is a strong, sour, or ammonia-like smell. Fresh snapper should have a mild, clean, ocean-like scent.
- Texture: If the flesh feels slimy, mushy, or is falling apart, it has likely spoiled. Fresh fish should be firm to the touch.
- Color: The vibrant, rosy color of fresh snapper will become dull, faded, or discolored when it goes bad.
7 Simple Snapper Home Remedies
Are there any less-known tips to unlock the nutritious profile of snapper? The following snapper remedies can have a positive effect on overall well-being.
- Snapper Bone Broth for Joint Support: Gently simmer the leftover bones and head of a snapper in water with a splash of apple cider vinegar for several hours. The resulting broth is rich in collagen and minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which can help support joint health. Strain the broth and store it in the refrigerator for up to 5 days or freeze it for later use as a base for soups and stews.
- Omega-3 Infused Snapper Oil: Slowly poach fresh snapper fillets in high-quality extra-virgin olive oil with garlic and herbs over very low heat until the fish is just cooked through. The heart-healthy fats from the fish will infuse into the oil. Use the tender fish immediately and store the leftover strained oil in a sealed jar in the refrigerator for up to a week to use in salad dressings or for drizzling over vegetables.
- Post-Workout Snapper Protein Mash: Steam a snapper fillet until cooked, then flake it into a bowl. Mash the fish with a small amount of olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper. This simple, easily digestible preparation delivers a powerful dose of high-quality protein to aid muscle repair and recovery after exercise. It can be eaten as is or spread on whole-grain crackers.
- Skin-Nourishing Collagen Bites: Instead of discarding the skin, pat it dry and bake it until crisp. The skin is a concentrated source of marine collagen, which is beneficial for skin elasticity. These crispy “chips” can be stored in an airtight container at room temperature for a day or two and eaten as a nutrient-dense snack.
- Immune-Boosting Snapper and Ginger Soup: Create a light, restorative soup by simmering snapper pieces in a broth made with fresh ginger, garlic, and turmeric. The high selenium content in snapper, combined with the anti-inflammatory properties of the spices, makes this a comforting remedy to support the immune system during the cold season.
- Thyroid-Support Mineral Powder: Carefully clean and dehydrate snapper bones in a low oven until they are brittle. Grind the bones into a fine powder using a spice grinder. This powder is a concentrated source of iodine and selenium, two minerals essential for healthy thyroid function. A very small pinch can be added to smoothies or soups as a natural mineral supplement.
- Calming Magnesium Snapper Salad: Combine chilled, cooked snapper with magnesium-rich foods like spinach, avocado, and almonds. Snapper itself contains magnesium, which plays a role in nerve function and can have a calming effect on the nervous system. This remedy is a simple meal to help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
Snapper and Weight Management

There are multiple health benefits, and home remedies using snapper, but what is their role in weight management? This section will analyze snapper’s potential impact on weight loss, low-calorie diets, satiety, and metabolism.
Can snapper help with weight loss?
Yes, snapper can be an excellent component of a weight-loss diet. Its primary contribution comes from its high protein and low-calorie profile. Numerous studies have shown that diets higher in protein can lead to greater weight loss and fat loss compared to lower-protein diets. The protein in snapper helps preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolic rate.
Snapper in low-calorie diets
Snapper is a perfect fit for low-calorie diets. A typical 100-gram (3.5-ounce) serving of cooked snapper contains only about 128 calories. This allows for a substantial, satisfying portion of food without a high caloric cost. Its leanness means it provides pure protein and nutrients with very little fat, making it easy to incorporate into a calorie-controlled eating plan without sacrificing volume or nutritional value.
Snapper and satiety
Satiety, or the feeling of fullness and satisfaction after a meal, is a critical factor in successful weight management. Protein is widely recognized as the most satiating macronutrient. Research has consistently demonstrated that high-protein meals reduce hunger and subsequent calorie intake at later meals. The 26 grams of protein in a 100-gram serving of snapper significantly enhances satiety, helping to curb cravings and prevent overeating throughout the day.
Snapper and metabolism
Including snapper in your diet can have a positive effect on your metabolism. The body uses more energy to digest protein than it does to digest fats or carbohydrates—a phenomenon known as the thermic effect of food (TEF). This means that simply by eating a high-protein food like snapper, you slightly increase your daily calorie burn. Furthermore, snapper is rich in B vitamins, such as B12 and B6, which play an essential role in energy metabolism by helping your body convert food into usable energy.
Snapper for Health Conditions
While weight management is important, do snapper have an effect in more serious health conditions? Here’s what the scientific literature has to say:
Snapper and diabetes
Snapper is an excellent food choice for individuals managing diabetes or prediabetes. As a fish, it contains zero carbohydrates, meaning it will not cause a spike in blood glucose levels. Its high protein content also helps with blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, the omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like snapper have been studied for their role in improving insulin sensitivity, which is a key factor in managing type 2 diabetes.
Snapper and heart health
The evidence supporting fish consumption for heart health is robust. Snapper is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are strongly linked to a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. According to the American Heart Association, regular fish consumption may significantly decrease your risk of heart disease, atherosclerosis (the hardening of arteries), and high blood cholesterol. Snapper is also low in sodium and saturated fat and provides a high concentration of potassium (444 mg per 3-ounce serving), a mineral known to help lower blood pressure (Mandel et al., 2015).
Snapper and digestive issues
Snapper is known to be an easily digestible protein. This makes it a suitable option for individuals with sensitive digestive systems. Its nutrients can aid in reducing inflammation within the digestive tract, potentially leading to better nutrient absorption and a decreased risk of stomach problems.
Snapper and inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many diseases. Snapper is a fantastic source of anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats can help reduce systemic inflammation throughout the body. Additionally, snapper is packed with selenium, a powerful antioxidant. Antioxidants work to neutralize free radicals, which can cause cellular damage that contributes to inflammatory conditions like arthritis (Harris-Ray, 2024).
Snapper and cancer prevention
The link between snapper and cancer prevention is primarily associated with its high selenium content. A single serving of snapper can provide nearly 70% of the daily recommended amount of selenium. Selenium is a crucial component of the body’s antioxidant defence system. Some studies suggest that selenium may help prevent free radical compounds from causing the DNA damage that can potentially lead to certain types of cancer (AquaPazza, n.d.).
The evidence suggests that the rich nutritional profile of snapper, particularly its omega-3 fatty acids and selenium content, offers protective benefits across several health categories, from cardiovascular health to cellular protection.
| Health Category | Benefits | Type of Study/Evidence | Quality of Evidence | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Health | Reduces risk of heart disease, lowers blood pressure and cholesterol. | Multiple large-scale observational studies and clinical trials. | High | Mandel et al. (2015); Foodstruct (n.d.) |
| Inflammation | Omega-3s reduce systemic inflammation; selenium acts as an antioxidant. | Established biological mechanisms and clinical studies. | Moderate to High | Palumbo (2020) |
| Thyroid Health | High selenium content is required for proper thyroid gland function. | Pre-clinical studies (animal models) and established nutritional science. | Moderate | Harris-Ray (2024) |
| Brain Health | Omega-3s and nutrients support cognitive function and cell health. | Pre-clinical studies and observational data. | Moderate | Harris-Ray (2024); Palumbo (2020) |
| Cancer Prevention | Selenium’s antioxidant properties may prevent DNA damage. | Mechanistic and epidemiological studies (suggestive, not conclusive). | Low to Moderate | AquaPazza (n.d.) |
Final Thoughts on Snapper Nutrition
This article has provided an in-depth look at the world of snapper, covering everything from the 13 effective health benefits of snapper and detailed snapper nutrition facts, to potential snapper risks and side effects and suitable snapper substitutes. We explored various popular snapper diets, offered essential snapper storage tips, shared 7 simple snapper home remedies, and analyzed the role of snapper and weight management and its impact on major snapper for health conditions.
- A single 3-ounce serving of snapper contains 59% of your daily selenium needs.
- Snapper is a Vitamin B12 powerhouse, delivering 50% of the daily value in just 3 ounces.
- It is a zero-carb food, making it ideal for low-carb and keto diets.
- Snapper is a lean protein, with over 22 grams of protein and only 109 calories per 3-ounce serving.
- Fresh, raw snapper should be consumed within 1 to 2 days when stored in the refrigerator.
- The omega-3 fatty acids in snapper are strongly linked to a reduced risk of heart disease.
This content was last updated in March 2026.
Follow Anai.ai to stay informed about the latest nutrition and well-being news, tips and articles.
Snapper Nutrition FAQs
This section provides concise, data-driven answers to common questions about snapper. It covers key topics like its health benefits, dietary safety for humans and pets, and proper storage. This guide helps you make informed decisions about including snapper in your diet.
What is snapper good for?
Snapper is exceptionally good for supporting overall health due to its dense nutritional profile. It is excellent for heart health, thanks to its high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, and for thyroid function, as a single 100-gram serving provides nearly 90% of the daily value for selenium. This lean fish also aids in weight management and boosts the immune system, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Is snapper healthy?
Yes, snapper is an incredibly healthy food choice. It is a low-calorie, high-protein fish, packing an impressive 26 grams of protein into just 128 calories per 100-gram serving. Furthermore, it is loaded with essential nutrients, including a remarkable 146% of the daily value for Vitamin B12, which is vital for nerve function and the production of red blood cells.
Is snapper fattening?
No, snapper is not fattening; it is an exceptionally lean fish. A 100-gram portion of cooked snapper contains only 1.7 grams of total fat and is very low in saturated fat. The majority of its fat content consists of healthy polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats, including beneficial omega-3s. This makes it an ideal protein source for those on a low-fat or calorie-conscious diet.
Who should avoid snapper?
Individuals with a fish allergy should completely avoid snapper to prevent potentially severe reactions. Pregnant women, those who are breastfeeding, and young children should consume snapper in moderation—no more than one to two servings per week—due to the potential for mercury content. Additionally, people should avoid eating very large snapper caught from reef environments to minimize the risk of ciguatera fish poisoning.
Can I eat snapper daily?
While snapper is very nutritious, eating it daily is not recommended. The primary concern is the potential accumulation of mercury over time. Health organizations generally advise consuming fish like snapper one to two times per week as part of a varied diet that includes other types of low-mercury fish and protein sources. This approach ensures you get the benefits of fish while minimizing potential risks.
Can dogs eat snapper?
Yes, dogs can eat snapper, but it must be prepared correctly and given in moderation. The fish must be thoroughly cooked without any salt, seasonings, garlic, or onions, and all bones must be meticulously removed to prevent choking or internal injury. Snapper can be a healthy treat for dogs as it provides high-quality protein and beneficial omega-3 fatty acids, which support a healthy coat and skin.
Can cats eat snapper?
Yes, cats can eat snapper in moderation as a healthy treat. It must be cooked plain—without salt, spices, or oils—and all bones must be removed to prevent choking or internal damage. Snapper offers a good source of lean protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which can help support a cat’s skin and coat health. However, it should only be a small part of a cat’s diet and not a replacement for their nutritionally complete cat food.
How long do snapper last in the fridge?
The shelf life of snapper in the refrigerator is quite short, so it should be handled promptly. Fresh, raw snapper is best when used within 1 to 2 days of purchase when stored correctly at a temperature at or below 40°F (4°C). Once cooked, snapper leftovers can be safely kept in an airtight container in the fridge for 3 to 4 days.
Can you freeze snapper?
Yes, you can absolutely freeze snapper to extend its shelf life significantly. When properly prepared and stored in an airtight, moisture-proof package, raw snapper can maintain its best quality for 6 to 8 months in a freezer set at 0°F (-18°C). For optimal results, vacuum-sealing the fish before freezing is the best method to prevent freezer burn and preserve its texture and flavor.
How to tell if snapper is bad?
You can tell if snapper has gone bad by using your senses. The most obvious sign is a strong, sour, or ammonia-like odor instead of a mild, fresh ocean scent. The fish’s texture will also change from firm to soft, mushy, or slimy. Visually, spoiled snapper will lose its vibrant color, appearing dull, discolored, or having dark spots.
How long is snapper good for?
Snapper is good for a very limited time when fresh, but lasts much longer when frozen. In the refrigerator, you have a window of 1 to 2 days to cook raw snapper, while cooked snapper lasts 3 to 4 days. If you freeze it, its quality is best for up to 8 months, and it can remain safe to eat for even longer if continuously frozen.
How to keep snapper fresh?
To keep snapper fresh, it is critical to store it at a cold temperature, ideally around 32°F (0°C). The best method is to remove the fish from its store packaging, rinse and pat it completely dry, and then seal it in a zip-top bag with all the air pressed out. Place this bag on a bed of ice in a container on the lowest shelf of your refrigerator, which is the coldest part, and replenish the ice as it melts.

